Memory dumps on 64bit server
Memory dump is a snapshot of process memory written in file. They are useful in many ways to troubleshoot freezes, performance issues or crashes. To get dump manually you have to be careful if you are running 64 bit OS and your process is 32 bit.
How to take dump
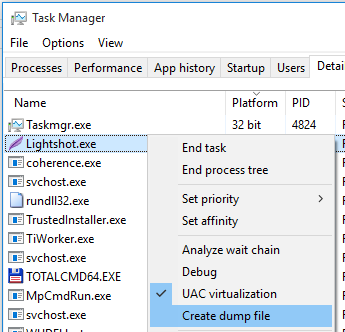
Simplest way to take process dump is Windows task manager. You need to locate process and choose “Create dump file” in context menu. Task manager will write dump file to temporary folder and show you path to the dump.
 In most cases you can then quickly open dump folder in explorer if you type %temp% as folder path.
In most cases you can then quickly open dump folder in explorer if you type %temp% as folder path.
32bit task manager
It is very important to match platform and use 32 bit task manager to take dumps of 32 bit processes. Same applies for 64 bit. When you are on 64 bit OS, by default it launches 64 bit task manager, so when you need 32 bit version, you have to run it manually using %Windir%\SysWOW64\taskmgr.exe
Please note: you can run only 1 task manager at a time, so if you’ve launched 64 bit version and then try to launch 32 bit one, it won’t launch, so first you should close all existent instances. If you use wrong task manager to take dump, most likely it will just not open properly.
Determine whether process is 32 or 64 bit
Starting from Windows 8, the task manager writes “(32 bit)” in processes tab for all 32 bit processes. You can also add “Platform” column on details tab to show the same information.
Happy dumps analysis!
